一、 javascript 6种常见继承
在解释 inherits 函数之前先来再次熟悉一下js6种继承方式。熟悉后再来看 inherits 函数中的继承实现。
1. 原型链继承
这种继承的最大特点是:子类的原型继承父类的实例对象
例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| function SuperType() {
this.property = true;
}
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function() {
return this.property;
};
function SubType() {
this.subproperty = false;
}
SubType.prototype = new SuperType();
SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function() {
return this.subproperty;
}
let instance1 = new SubType();
console.log(instance1.getSuperValue());
|
优点:
- 引用类型的方法被所有实例共享,也就是说一个方法,可以到处使用。
缺点:
- 子类实例上共享父类所有的引用类型的实例属性,进而导致多个实例操作同一个实例属性造成数据混乱。
- 子类型在实例化时不能给父类型的构造函数传参。
如何理解共享父类的引用类型的实例属性会导致数据混乱问题?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| function SuperZoo() {
this.zoo = ['dog', 'pig'];
}
SuperZoo.prototype.pushAnimal = function(animal) {
return this.zoo.push(animal);
};
SuperZoo.prototype.getAnimal = function() {
return this.zoo;
};
function SubZoo() {
this.isDoorClose = false;
}
SubZoo.prototype = new SuperZoo();
SubZoo.prototype.isDoorClose = function() {
return this.isDoorClose;
}
let instance1 = new SubZoo();
instance1.pushAnimal('duck');
console.log(instance1.getAnimal());
let instance2 = new SubZoo();
instance1.pushAnimal('swallow');
console.log(instance1.getAnimal());
|
从上述代码中可以看出,两个实例(instance1、instance2)操作了同一个父类实例属性,这里只是向里面推入数据,如果有多个实例对该实例共享属性做增删改查,那么最后得出的结果会和预期不符。
2. 借用构造函数继承
为了解决‘原型链继承’中引用类型实例属性带来的数据混乱问题,进而出现借用构造函数继承(盗用构造函数/对象伪装/经典继承)
这种继承的最大特点是:在子类构造函数中调用父类构造函数,可以传递参数
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name;
}
function SubType(name) {
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = 29;
}
let instance1 = new SubType('kh-demo');
console.log(instance1);
|
优点
- 可以实现属性继承
- 子类型创建实例时可以给父类型传递参数
缺点
- 没有继承父类型的原型,所以原型上的属性和方法无法使用
- 由于没有继承父类型的原型,所以不同实例不能重用函数
由于借用构造函数继承的缺点导致了它在处理继承问题时不能单独使用。因此引出了“组合继承”(下文会有介绍)
如何理解没有继承父类型的原型,所以原型上的属性和方法无法使用?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name;
}
SuperType.prototype.getName = function() {
return this.name;
}
SuperType.prototype.kh = 'demo';
function SubType(name) {
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = 29;
}
let instance1 = new SubType('kh-demo');
console.log(instance1.getName(), instance1.kh);
|
上面示例中因为只是继承了父类的实例属性和方法,所有父类原型链上的方法和属性时访问不到的。
3. 组合继承
组合继承(伪经典继承)综合了原型链和借用构造函数,将两者的优点集中起来。它的思路是使用原型链继承原型上的属性和方法,使用借用构造函数继承实例属性。这样既可以把方法定义在原型上以实现重用,又可以让每个实例都有自己的属性。
这种继承的最大特点是:在子类构造函数中调用父类构造函数以及子类原型继承父类的实例对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function SuperType(name){
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() {
return this.name;
};
function SubType(name, age){
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
SubType.prototype = new SuperType();
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() {
this.age;
};
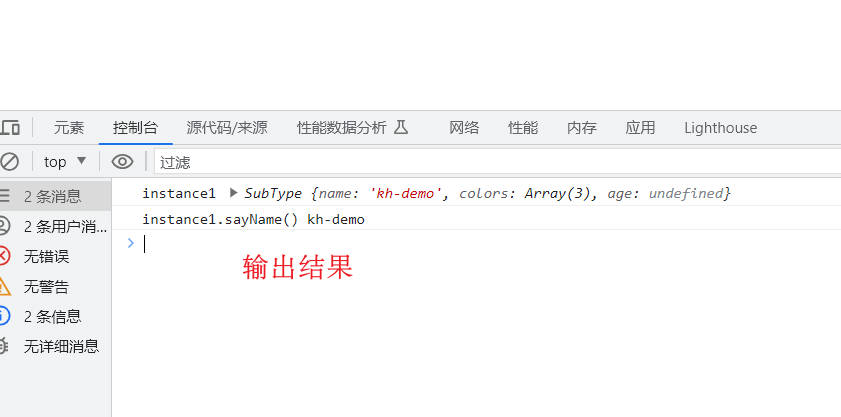
let instance1 = new SubType('kh-demo');
console.log('instance1', instance1);
console.log('instance1.sayName()', instance1.sayName());
|
优点
- 拥有原型链继承和构造函数继承的所有优点
缺点
1.缺点也很明显就是调用两次父级构造函数:一次是在创建子类原型的时候,另一次是在子类构造函数内部。
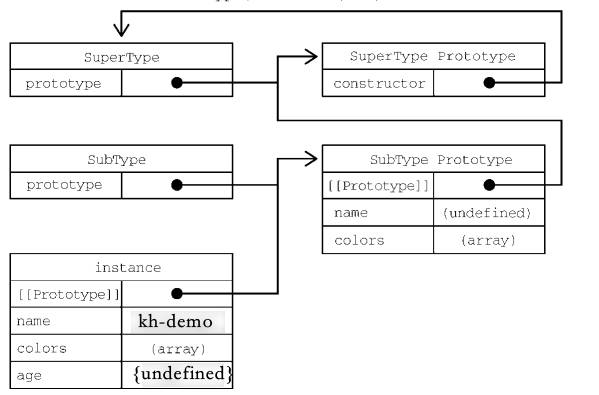
注意:因为SuperType函数在两个地方分别调用,导致了它的实例属性在两个地方都存在。如下图所示
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function SuperType(name){
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() {
return this.name;
};
function SubType(name, age){
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
SubType.prototype = new SuperType();
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() {
this.age;
};
let instance1 = new SubType('kh-demo');
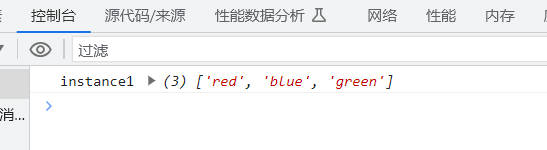
delete instance1.colors;
console.log('instance1', instance1.colors);
|
4. 原型式继承
这种继承的最大特点是:原型式继承的object方法本质上是对参数对象的一个浅复制
如何理解对参数对象的一个浅复制呐?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| function object(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
let person = {
name: "Nicholas",
friends: ["Shelby", "Court", "Van"]
};
let anotherPerson = object(person);
anotherPerson.name = "Greg";
anotherPerson.friends.push("Rob");
let yetAnotherPerson = object(person);
yetAnotherPerson.name = "Linda";
yetAnotherPerson.friends.push("Barbie");
console.log(person.friends);
|
es5 中也可以使用Object.create() 方法来创建
优点
- 父类方法可以复用。
缺点
- 父类的引用属性会被所有子类实例共享
5. 寄生式继承
这种继承的最大特点是:二次封装原型式继承(在原型式继承基础上拓展属性和方法)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| function object(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function createAnother(original){
let clone = object(original);
clone.sayHi = function() {
return "hi";
};
clone.newPo = 'kh-demo';
return clone;
}
let person = {
name: "Nicholas",
friends: ["Shelby", "Court", "Van"]
};
let instance1 = createAnother(person);
console.log(instance1);
|
缺点
- 跟借用构造函数模式一样,每次创建对象都会创建一遍方法。
6. 寄生组合继承
这种继承的最大特点是:它是寄生式继承+借用构造函数的组合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function object(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function inheritPrototype(subType, superType){
const prototype = object(superType.prototype);
prototype.constructor = subType;
subType.prototype = prototype;
}
|
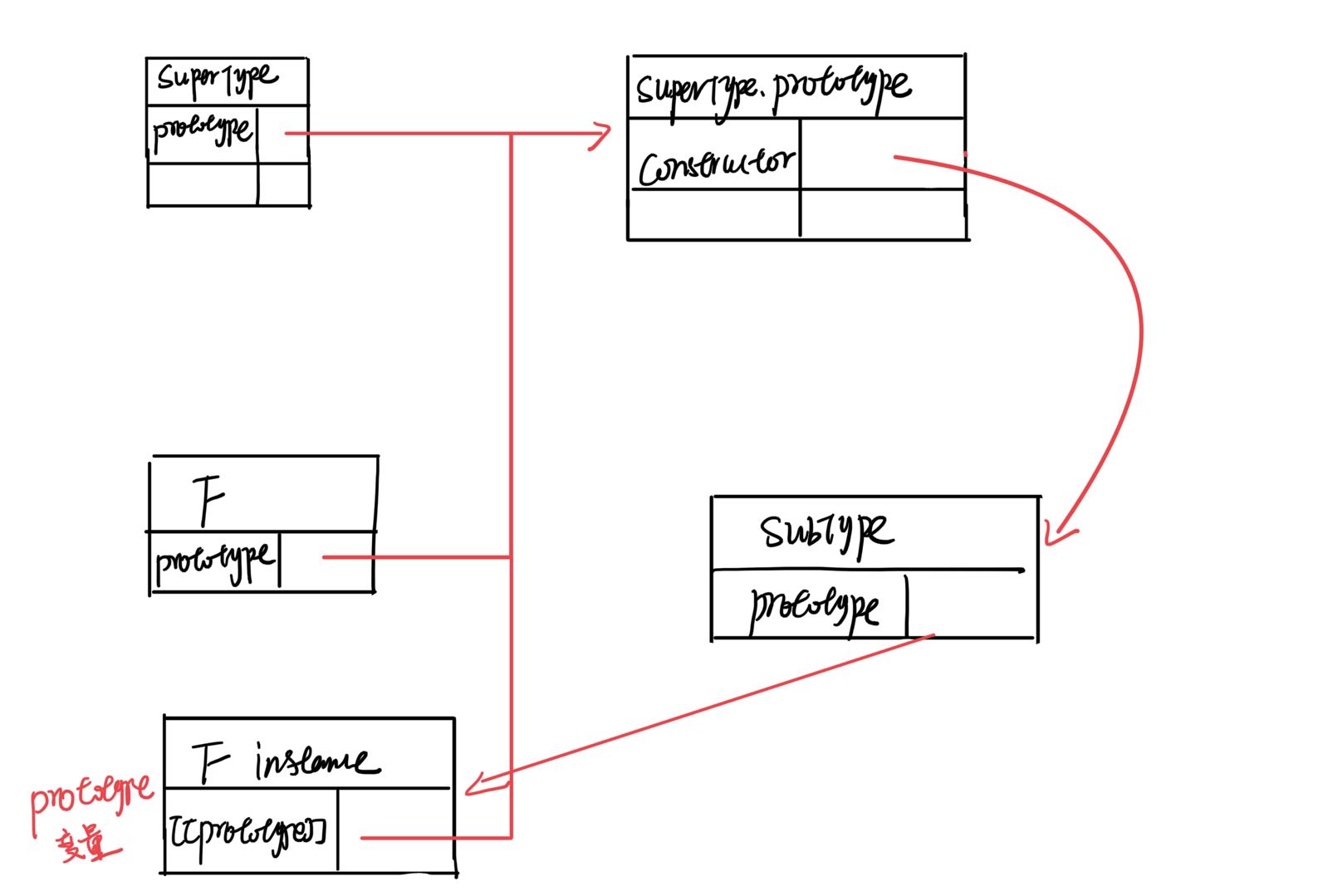
inheritPrototype()函数实现了寄生式组合继承的核心逻辑。这个函数接收两个参数:子类构造函数和父类构造函数。在这个函数内部,第一步是创建父类原型的一个副本。然后,给返回的prototype 对象设置 constructor 属性,解决由于重写原型导致默认 constructor 丢失的问题。最后将新创建的对象赋值给子类型的原型。
通过调用 inheritPrototype() 函数就可以实现子类的原型赋值,如下图
寄生组合继承完整代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| function object(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function inheritPrototype(subType, superType){
const prototype = object(superType.prototype);
prototype.constructor = subType;
subType.prototype = prototype;
}
function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() {
return this.name;
};
function SubType(name, age) {
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() {
return this.age;
};
inheritPrototype(SubType, SuperType);
|
优点
- 是一种完美的继承方式
二、inherits 源码解读
重温了js常见的6种继承后,看一下 inherits 函数源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
function inherits(subClass, superClass) {
var subClassProto = subClass.prototype;
var F = new Function();
F.prototype = superClass.prototype;
subClass.prototype = new F();
subClass.prototype.constructor = subClass;
extend(subClass.prototype, subClassProto);
}
|
从 inherits 函数源码可以看出,它使用的继承和寄生组合继承核心逻辑一致。只不过这里使用的代码风格不一样罢了(其实是另一种实现)。
比如
- 使用 Function 构造函数创建 Function 对象。在寄生组合继承中使用 function F() {} 直接定义。
- 在寄生组合继承中使用 object() 函数完成的内容和F.prototype = superClass.prototype; new F() 一致
最后通过 extend() 函数把 subClassProto 上的属性和方法复制到 subClass.prototype 上
三、 示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| function SuperType() {
this.name = 'super-demo';
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() {
return 'SuperType-sayName';
};
function SubType() {
this.age = 'sub-age';
}
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() {
return this.age;
};
inherits(SubType, SuperType);
let subInstance = new SubType();
console.log(subInstance.sayName());
|








